Have you seen the inspirational quote “a diamond is merely a lump of coal that did well under pressure”? While I agree with the sentiment of not giving up, to keep going, and that we can evolve into something more beautiful by growing through hard times, the saying is bogus.
Diamonds are not coal under pressure. I assume that this comes from the fact that they are both composed of carbon, but the origin story of diamonds is actually way cooler.

Janine Krippner
Society has been convinced that diamonds are a girl’s best friend, and you must show your love through diamonds. Many reject this now, especially knowing the harm that diamond mining causes (please make sure they are ethically sourced), and the financial pressure this places on people.
Diamonds were brought to the Earth’s surface during mostly violent eruptions a very long time ago.
Diamonds do form under immense pressure, but in the mantle, around 200km or deeper. Much deeper than coal would survive. A rare magma type called Kimberlite rips apart chunks of mantle rock that contains the diamonds and carries them rapidly towards the surface. This is some of the deepest magma that reaches the surface, and by rapid, I mean it may travel around 150-200km upwards in hours to a couple of days.
There has been a great deal of research done on Kimberlites partly because of their economic importance, partly because we love to understand every type of eruption, and also because they help us understand the deeper parts of our Earth. Diamonds are the hardest mineral, and with their thermal conductivity this makes them very useful. Large amounts of diamonds are used for industrial processes like drilling, cutting, and polishing. They are not the glamourous diamonds we think of.
Scientists have figured out that kimberlite eruptions may be related to the process of tectonic plates pulling apart, occurring 20-30 million years after the process begins. Kimberlites at the surface are millions to 2.5 billion years old, we aren’t even a blink of an eye in these timescales.
On the smaller scale, many diamonds contain small dots or imperfections that make them even more interesting (and cheaper). These are tiny time capsules called fluid or melt inclusions that were trapped inside as the diamond grew. Studying inclusions is an important part of unravelling their ancient stories. We understand that the magma likely started out at around 1350 to 1450°C, then cooled by a few hundred degrees during their ascent. This changes the magma in significant ways while it is moving. Just like other magma, this doesn’t always lead to an eruption. We also have intrusions that cooled to solid rock below ground and have since been exposed at the surface by processes including erosion over many millions of years.
While the inspirational idea of coal turning to diamond may be rubbish, diamonds are incredible parts of ancient eruptions of rare magmas sourced from deep below our feet, that formed in very high pressures and temperatures, then were brought to the surface at amazing speeds. A diamond ring symbolically means forever, and compared to our wee lifetimes, they pretty much are.
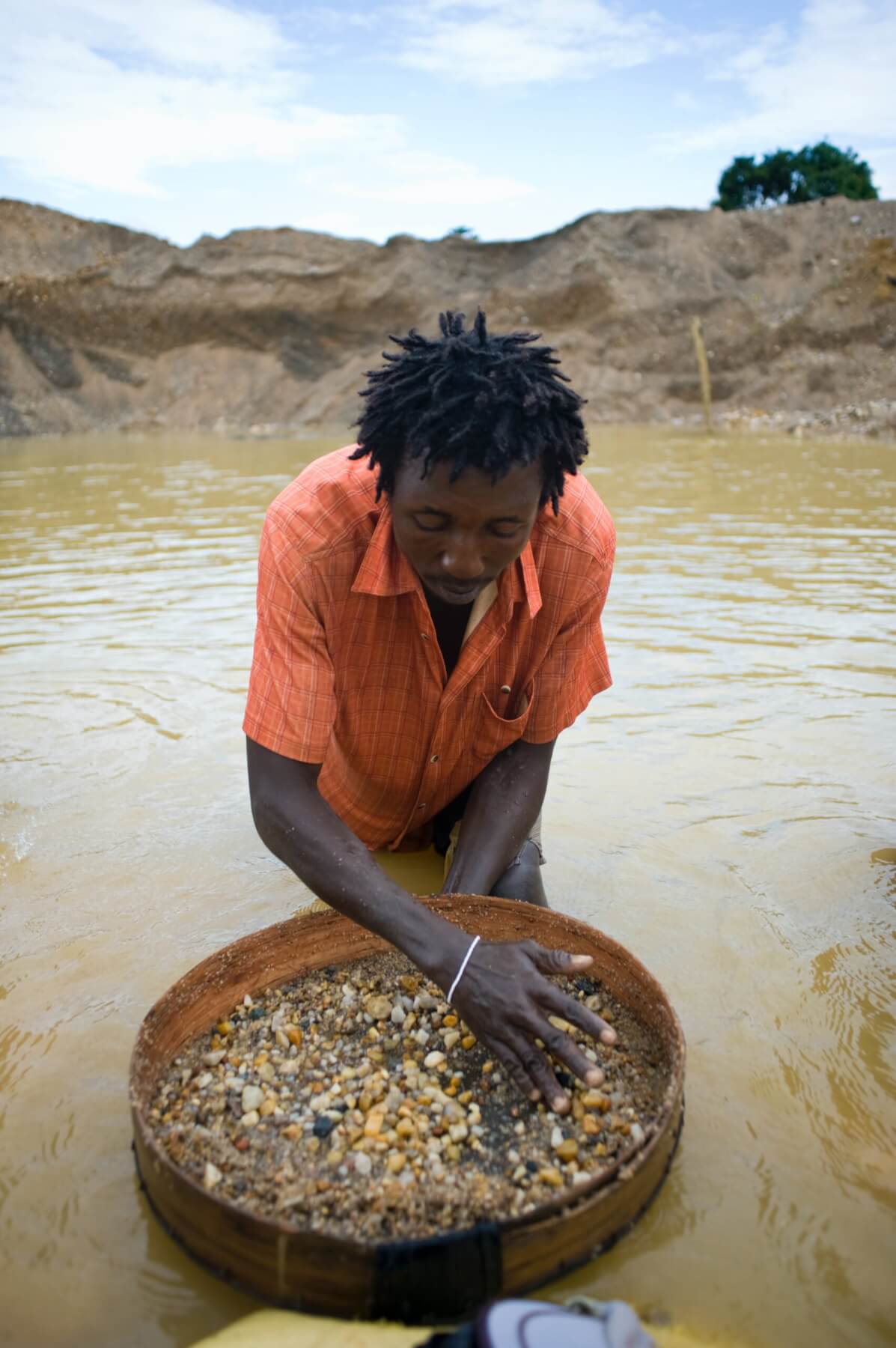

A man searching for diamonds in Sierra Leonie. Photo: Sheku Koroma, Pexels.com